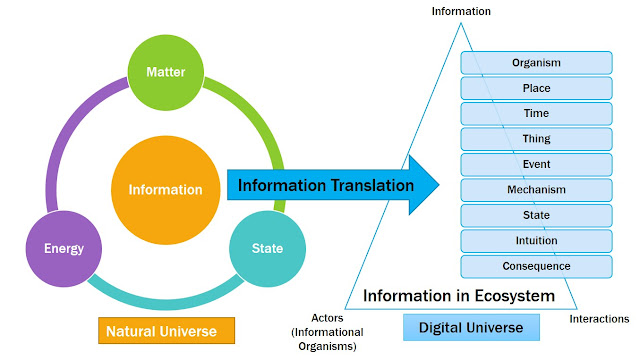
Future Beyond AI: Shifting focus form Artificial Intelligence (AI) to Human Augmentation (HA) via HSDD Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is gaining significant interest and hype across the globe. AI can be used for automation, content generation, conversation, decision-making and recommendations, and seems to promise several befits such as efficiency and productivity. Benefits are there, however, there are also increasing concerns about AI safety, ethics and its adverse impacts e.g. replacing people and their jobs. In this post, I will not boast about the AI and its related concepts such as Agentic AI and so on. I will focus on the future and a shift from AI to HA (Human Augmentation) for the greater good of people, peace and prosperity (e.g. value for countries, customers, businesses, staff and society). so let's begin with defining the concepts of HA or human augmentation? Human Augmentation (HA) Humans have the physical structure, sensors, motor skills and cognitive ability to think, store, communicate and perform actions for achieving mental and p...