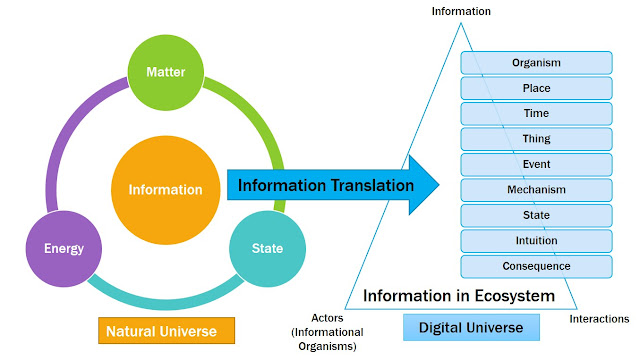
How to define information or data strategy?

Information or data strategy is a part of the overall corporate or business strategy. Information (including data) is an important strategic business asset. Thus, information assets should be managed and treated in the similar way as we manage other business assets. An actionable information strategy is required to for the effective handling of information across the enterprise, irrespective of their size, for achieving the business goals and reducing risk including compliance to regulatory requirements and standards. This post provides and discusses a simple and practical template for defining the information strategy as a part of the business or cooperate strategy. Information strategy can be defined at the ecosystem, enterprise, business function, business area or capability level as appropriate to your context and needs. Information strategy has following key 8 elements (Figure 1): Mission & Vision, Levers & Value Driver, Goals & Objective, Strategies & T...